Verifying a certificate should take seconds, not hours.
Yet most organizations still rely on phone calls, emails, and manual checks to confirm credentials. This creates delays, administrative burden, and leaves the door wide open for fraud.
Paper certificates and PDFs are easy to forge or alter. Fake degrees, manipulated certifications, and fraudulent credentials cost businesses billions every year. Worse, traditional verification methods can’t keep pace — contacting issuing bodies directly or relying on third-party services creates friction at every step.
QR Codes offer a better solution. When embedded in a certificate, a QR Code links directly to a secure verification page maintained by the issuing authority. One scan confirms authenticity in real time.
In this guide, we’ll show you how QR Codes enable instant, reliable certificate verification, and share best practices for implementation.
Table of contents
- Why is manual certificate verification slow and unreliable?
- How do QR Codes work to verify certificate authenticity?
- How to implement QR Codes for certificate verification
- A step-by-step guide to creating QR Codes for certificates
- Manage certificates over time using QR Codes
- How businesses use QR Codes on certificates (with real examples)
- Best practices for reliable QR Code-based certificate verification
- Verify certificates faster using TQRCG
- Frequently asked questions
Why is manual certificate verification slow and unreliable?
Traditional certificate verification was not designed for today’s speed or scale. It relies on outdated processes held together by manual effort, fragmented records, and trust that documents have not been falsified. Let’s look at some of the disadvantages of manual verification:
Manual verification wastes time
Only 20% of employers verify qualifications directly with issuing institutions. Most rely on paper certificates or PDFs at face value, largely because traditional verification is inefficient.
Emails go unanswered, records are scattered across departments, and there is no single source of truth. Employment verification alone can take one to three days in the best case and more than a week when employers are slow to respond. In regulated sectors like healthcare, credential checks can significantly slow recruitment, delaying hiring decisions, audits, and onboarding when speed matters most.
Fraud is easy
With basic design software, forged documents can pass visual inspection, especially when no verification step is enforced. Research suggests up to 75% of certificates circulating in parts of Africa may be falsified. Even with consent to verify, many background checks reveal fraudulent qualification claims.
Because most organizations do not consistently verify credentials, fake certificates often slip through. By the time fraud is detected, the damage is already done.
No standard verification process
Every issuing authority follows a different verification method. Some rely on email confirmations, others on portals or manual record checks. As a result, employers may spend 3 to 5 days per credential tracking information across emails, phone calls, and systems.
This fragmentation has real consequences. Many recruiters struggle to validate certificates because they must handle multiple formats, systems, and processes. Without a shared standard for verification, delays increase, costs rise, and fraud becomes harder to detect.
Trust erodes for everyone
When verification is slow and unreliable, even legitimate credentials are questioned. Employers grow skeptical, regulators demand more proof, and qualified candidates pay the price for a system that can’t distinguish between authentic certificates and fake ones.
QR Codes offer a tangible solution to many of the above problems related to certificate verification. Let’s see how.
How do QR Codes work to verify certificate authenticity?
A QR Code on a certificate does not, on its own, prove authenticity. Instead, it acts as a secure pointer to a verification source controlled by the issuing authority.
When scanned, the QR Code directs the verifier to verification data stored separately from the certificate document. This separation is important. While a certificate can be copied, shared, or printed, the verification record remains locked within the issuer’s system and cannot be altered by the recipient.
Even if someone duplicates a certificate perfectly, the verification page reveals the real status. It shows whether the certificate is valid, expired, revoked, or never issued.
How the verification process works
- When a certificate is issued, a unique record is created in a secure system.
- This record becomes the single source of truth for that certificate.
- A QR Code is then generated to link directly to this record.
- That QR Code is placed on the certificate you receive or share.
- When someone scans the QR Code on the certificate, they are redirected to a verification page.
- The system confirms the certificate’s authenticity and displays its current status instantly.
How to implement QR Codes for certificate verification
The real value of QR Codes lies not in the code itself, but in the verification system behind it. When implemented correctly, QR Codes connect certificates to live, issuer-controlled records that cannot be altered or faked.
Here’s how a well-designed QR Code verification system works.
Link each certificate to a unique digital record
Every certificate gets a unique identifier that connects to a master record in the issuer’s system. This record acts as the single source of truth.
When someone scans the QR Code, they’re checking the certificate against this source record, not the PDF layout or the printed document. If a name or detail is altered on the legitimate certificate, the QR Code still points to the original record, immediately exposing the mismatch.
Redirect to an issuer-controlled verification page
Scanning the QR Code takes the verifier to a verification page hosted and maintained by the issuing organization. This is where authenticity is confirmed.
The verification page checks the certificate against the issuer’s records, not the PDF or printed document itself. Because the data is controlled by the issuer, any copied or altered certificate is immediately flagged.
There is no need to email registrars, contact issuing offices, or rely on screenshots shared over messaging apps. Verification happens instantly, directly from the source.
Show issuer certificate and details in real time
The verification page displays key information such as the issuing authority, recipient name, and issue date. Because this data is pulled live from the issuer’s system, verifiers see the most current information, not an outdated copy of the certificate.
Services like Higher Education Degree Datacheck show how real-time verification can scale, handling large volumes of checks without manual intervention.
Display the current status of the certificate
Certificate details alone are not enough. A credential may look valid on paper but still be expired, suspended, or revoked.
QR Code–based verification surfaces the certificate’s real-time status at the moment of scanning, clearly showing whether it is active, expired, or no longer valid. This ensures verifiers are not relying on dates printed on the certificate itself.
Many professional certifications, including those issued by Microsoft and Amazon Web Services, follow this model. The physical certificate is largely symbolic, while the QR Code-linked record serves as the definitive proof of validity.
Enable digital portability of credentials
QR Code–enabled certificates are easy to share across resumers, portfolio, email signatures, and platforms like LinkedIn. Anyone who scans the code sees a verified, up-to-date record without the need for additional documents or follow-ups.
For issuing organizations, this also increases visibility. As verified certificates are shared publicly, the issuer’s brand reaches wider audiences organically, while recipients feel more confident displaying credentials that can be instantly verified.
Now that you understand how QR Codes work within a verification system, let’s look at how to create QR Codes for your certificates quickly and effectively.
A step-by-step guide to creating QR Codes for certificates
Adding verification QR Codes to certificates doesn’t have to be complicated. The QR Code Generator (TQRCG) makes the process fast and intuitive, offering an all-in-one platform where you can create, customize, and track QR Codes without technical expertise.
Step 1: Log in and select your QR Code type
Go to TQRCG’s homepage to find QR Code types.
For certificate verification, you’ll typically choose between
- URL QR Code: Links directly to your online verification database or portal.
- PDF QR Code: A QR Code linking to a PDF can guide viewers to a digital copy of the certificate or more information on how to verify.
- Plain Text QR Code: A QR Code linking to plain text can help verify a certificate’s authenticity by providing key, issuer-verified details, such as the recipient’s name, certificate ID, issue date, and course.
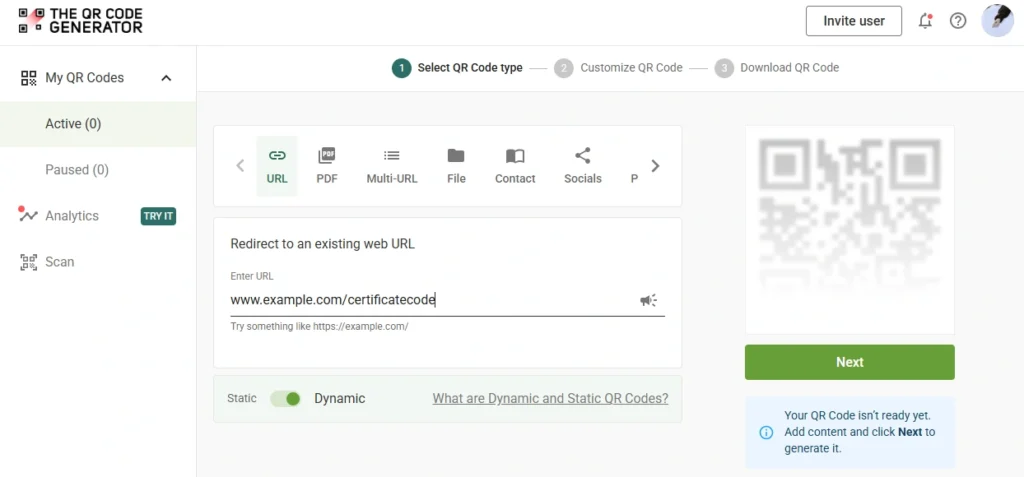
For certificates that need updatable links, select the dynamic option. Static QR Codes are fixed and can’t be changed once created, while dynamic QR Codes let you edit the destination later and track scans.
Step 2: Enter your verification URL or content
Input your certificate verification endpoint. This could be a unique URL connecting to your organization’s validation system. The platform automatically shortens longer URLs, keeping your QR Code aligned to QR Code best practices.
Step 3: Customize to match your brand
Add brand colors and, if you like, a small logo while keeping strong contrast for easy scanning.
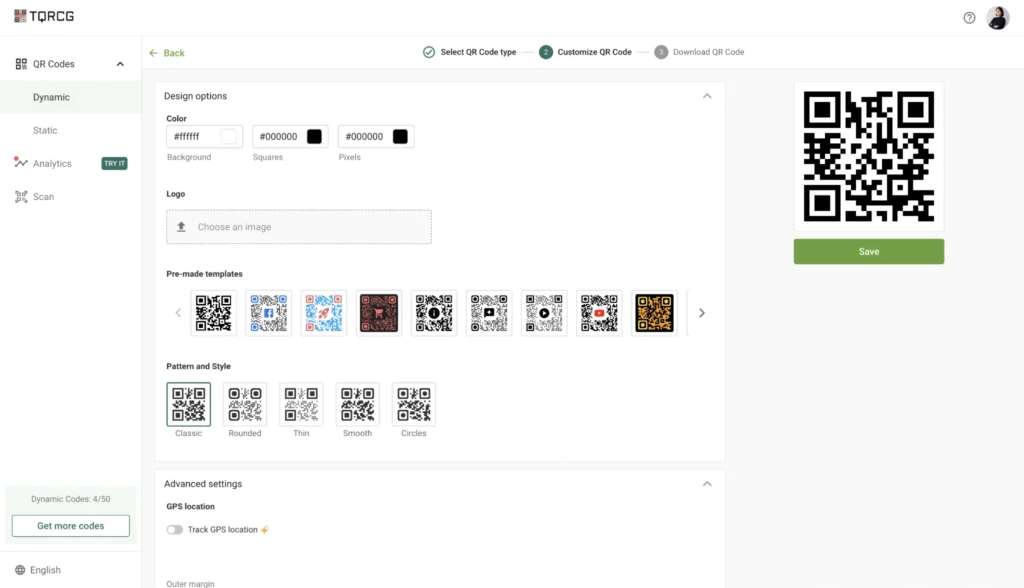
TQRCG has several design options that let you:
- Add your organization’s logo directly into the QR Code
- Adjust colors to match your brand palette
- Choose from multiple style templates, including classic, rounded, smooth, and circular patterns
- Modify the outer margin for better integration with certificate layouts
Step 4: Test and download
Always verify your QR Code functions correctly before printing. For proper scanning, follow a minimum QR Code size of 1 × 1 inch (2.5 × 2.5 cm), and for digital use, 300 × 300 pixels or higher for clarity.
Download options include:
- PNG format: Ideal for digital certificates and screen display
- SVG format: Vector files that allow unlimited scaling without quality loss
SVG QR Codes are best for printing on certificates because they scale without losing quality and remain sharp at any size.
Step 5: Monitor verification activity
Once your certificates are distributed, TQRCG’s analytics dashboard helps you understand how they’re being used. You can view essential QR Code metrics, including total and unique scans, scans by device usage, and geographic scan data by city, country, and GPS location.
Trackable QR Codes prove helpful here. This tracking is useful for identifying potential fraud patterns or understanding where your certificates are being verified most frequently.
Manage certificates over time using QR Codes
Once your certificates with QR Codes are out in the world, you don’t lose control of them. Here’s how to keep your credentials accurate and trustworthy without the hassle of reprinting
Revoke certificates without reprinting
When a certificate needs to be invalidated, you don’t need to track down every copy. Simply update the status in your backend system. The next time anyone scans that QR Code, they’ll see the certificate is no longer valid.
Traditional certificate verification can be surprisingly expensive; organizations often spend $25 to $200 per verification when you factor in paperwork, phone calls, third-party verifiers, and admin time. Real-time revocation through QR Codes cuts that overhead while protecting your organization from fraud.
Set up automatic expiration rules
Rather than manually tracking certificate expirations, let your verification system handle them. Configure your backend to automatically mark credentials as expired when they hit a predetermined date.
When you have safety certifications that need annual renewal or professional licenses, the system flags them automatically. Anyone scanning an expired certificate gets accurate information instantly.
Keep audit trails for accountability
Your verification system should maintain a complete history of each certificate. This matters more than you might think. If there’s ever a dispute about whether someone held valid credentials on a specific date, you’ll have documentation to prove it.
💡 Pro tip: Log every scan and status check. These records will help you during compliance reviews, legal disputes, or audits. They provide the transparency that regulators and stakeholders expect.
How businesses use QR Codes on certificates (with real examples)
Organizations across industries are already using QR Codes to fight fraud and simplify operations.
Employee training and compliance certificates
In construction and manufacturing, proving your workers have current safety training is the law. Each employee receives either a plastic photo-ID card or a rugged vinyl sticker for the front of their hard hat, both printed with the same unique QR Code. Any smartphone camera scans that code and loads the worker’s full credential page.
OSHA training providers have embraced this approach. If it is a plastic Outreach Training Program student or trainer card, scan the QR Code on the back to verify the training.

Platforms like Credential Verification Service (CVS) now issue safety certificates with QR Codes that managers and auditors can verify on-site in seconds.
Professional and industry certifications
Professional certifying bodies have caught on, too. Professional certification bodies like NPTEL include QR Codes on their certificates so anyone can scan and verify the credential online.

Government and public sector certificates
Government agencies handle some of the most sensitive documents imaginable, and QR Code verification is becoming standard practice. Digital birth certificates with QR Codes are now gaining traction. Hospitals now issue them directly, and they’re officially accepted by all government offices across the country.
In the Philippines, too, the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) now issues PSA certificates with QR Codes that link to PSA’s secure database, allowing real-time validation through the e-verification app.
Education and university certificates
Diploma fraud is a bigger problem than most people realize. This is because a paper document can easily be forged with advanced printing and copying technologies.
Universities are fighting back with QR Code verification. When an employer scans the code, they can confirm a candidate’s degree in seconds, rather than waiting weeks for the university to respond manually.
The French Ministry of Education also uses diplomas with QR Codes. When scanned, the QR Code shows a summary of personal information and grades.
Health and medical certificates
The healthcare industry probably saw the largest QR Code rollout in history during the COVID-19 pandemic. The EU Digital COVID Certificate entered into application throughout the EU in July 2021 and created a standardized system across 27 member states.
The validity and authenticity of the certificate are checked by verifying the digital signature of the issuing authority stored in the QR Code. Certificate signatures can be verified across the EU.

Beyond COVID certificates, QR Codes are being used in to medical field to authenticate health records, prescriptions, and medical certificates. A QR Code on a prescription allows pharmacies to verify authenticity instantly, helping to reduce the risk of forged prescriptions or fake medical certificates, ensuring patient safety and accuracy in treatment.
Now, let’s look at some best practices you need to keep in mind while you use QR Code-based certificate verification.
Best practices for reliable QR Code-based certificate verification
To ensure your certificates are trusted and secure, it’s important to follow proven methods when using QR Codes. These best practices help you verify quickly, accurately, and tamper-resistant every time.
Keep your verification systems in-house
Don’t hand over control of your verification URLs to third parties. When you host the destination yourself, you cut the risk of downtime, tampering, or someone else deciding your links no longer work.
Use dynamic QR Codes sparingly
If your verification link won’t change, stick with static codes. They’re simpler, more stable, and less prone to misrouting. Save dynamic codes for situations where you genuinely need the flexibility to update destinations later.
Connect to real-time backend checks
Static “certificate information” pages are sitting ducks for fraud. Link your QR Codes to a backend that performs live validation, such as checking revocation status, expiration dates, and current records with every scan.
Watch for red flags in scan activity
Set up monitoring to catch unusual patterns. Look for the same certificate scanned hundreds of times, verification attempts from unexpected countries, or spikes in activity that don’t match your issuance volume. These signals can help you spot abuse before it becomes a problem.
Verify certificates faster using TQRCG
A QR Code alone doesn’t prove a certificate is real. What it does is connect the person scanning to a system you control — one that can confirm authenticity, show current status, and flag anything that’s been revoked or expired.
The QR Code Generator (TQRCG) lets you create professional, trackable QR Codes in minutes. With built-in analytics, customization options, and support for dynamic codes, it’s a practical first step for organizations looking to add verification to their certificates.
You need to understand what makes this platform right for certificate verification. TQRCG has free unlimited static QR Codes. This makes it accessible for educational institutions, training providers, and businesses issuing credentials.
Other key advantages include two free dynamic QR Codes per user with lifetime validity and high-resolution downloads and support for multiple QR Code formats, and integrated analytics to track performance.
Sign up to create your free verification QR Code at TQRCG!
Frequently asked questions
The QR Code just points to your verification system. When someone scans a copied code, they’ll still see whether the certificate is valid, expired, or revoked. The authenticity lives in your backend, not in the code itself.
Usually, this means something’s off with your link or server. If you use a dynamic QR Code and host the verification yourself, fixing it is straightforward. Update the destination without reprinting a single certificate. This is exactly why controlling your own systems matters.
It shouldn’t. Best practice is to use a QR Code to link to a secure record in your database rather than embedding sensitive data directly. That way, personal details remain protected on your servers and are revealed only during legitimate verification.
As long as anyone might need to check the certificate. For professional credentials or compliance documents, that could mean years. Build your backend with longevity in mind, and those links will continue to return accurate, real-time information throughout the certificate’s lifecycle.
Yes, when they come from a recognized issuer with a properly maintained verification system. The QR Code itself isn’t legal proof; it’s the connection to your authoritative records that gives the certificate its legitimacy. Courts, regulators, and employers care about the source, and the QR Code just makes verification faster.