A boutique clothing store once printed stylish QR Codes on its product tags, linking to short styling videos. The tags looked stunning, and the QR Code blended into the logo design.
But, only a small percentage of customers could successfully scan the QR Codes. Others either gave up or had to ask staff for help, creating bottlenecks during busy periods. As a result, the store missed out on potential upsells.
Why did this happen? Decorative elements had been placed too close (within two modules of the QR Code edge), violating the industry’s minimum “four-module” quiet zone rule.
This example shows a common issue: a QR Code might scan in perfect conditions but fail repeatedly in the real world if its quiet zone is compromised. Let’s explore what the quiet zone is, why it matters, and how to get it right.
Table of contents
- What is a QR Code quiet zone?
- Why do we need quiet zones on QR Codes?
- The 4-module rule: Technical requirements for QR Code quiet zones
- What are the most common reasons for QR Code quiet zone violations?
- Techniques to ensure perfect quiet zone management (+ free checklist)
- Best practices to ensure a QR Code quiet zone across all mediums
- Scan-perfect QR Codes with TQRCG
- Frequently asked questions
What is a QR Code quiet zone?
The quiet zone is the blank, unprinted space surrounding a QR Code. It is a buffer that helps scanners detect where the code starts and stops. Without it, the scanner’s edge detection fails, leading to missed scans.
Think of it like page margins. Just as margins make a document easier to read, a quiet zone makes it easier for cameras to recognize and decode a QR Code.
A proper quiet zone must be:
- Uniform: The exact width on all four sides
- Unprinted: Free of design elements, text, or patterns
- High contrast: Typically white or very light colored against the QR Code’s dark elements
Remember, it is not just an empty space but a functional part of a QR Code’s design.
Why do we need quiet zones on QR Codes?
Modern cameras and scanning apps rely on edge detection algorithms to locate and read QR Codes. These algorithms scan for specific patterns that indicate QR Code boundaries.
Here’s what happens when you scan:
- Edge detection: Finds high contrast transitions marking QR Code boundaries
- Pattern recognition: Looks for the three finder patterns in QR Code corners
- Boundary calculation: Determines the exact code perimeter
- Data extraction: Reads the information encoded within the boundary
Without adequate quiet zone space, step one fails. The scanner can’t distinguish between your QR Code and surrounding design elements, causing the entire process to break down.
This explains why QR Codes sometimes scan successfully in perfect conditions but fail in real-world scenarios. Professional scanners in controlled environments might overcome minor quiet zone violations, while smartphone cameras in variable lighting with different angles cannot.
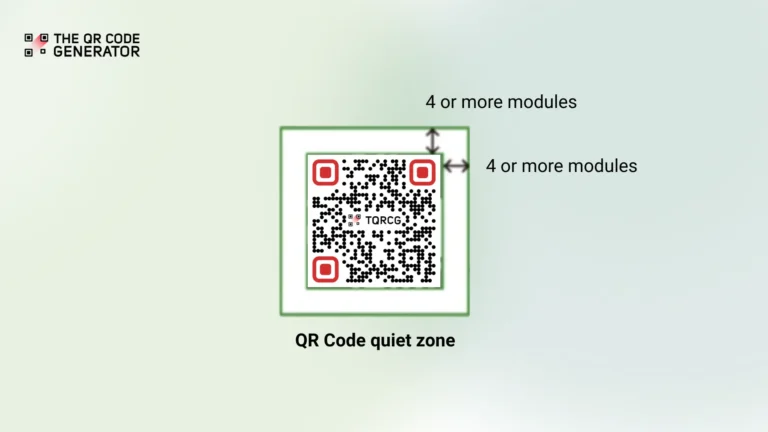
The 4-module rule: Technical requirements for QR Code quiet zones
The international standard for QR Codes, ISO/IEC 18004, specifies requirements for reliable scanning performance. These requirements are commonly called the four-module standard.
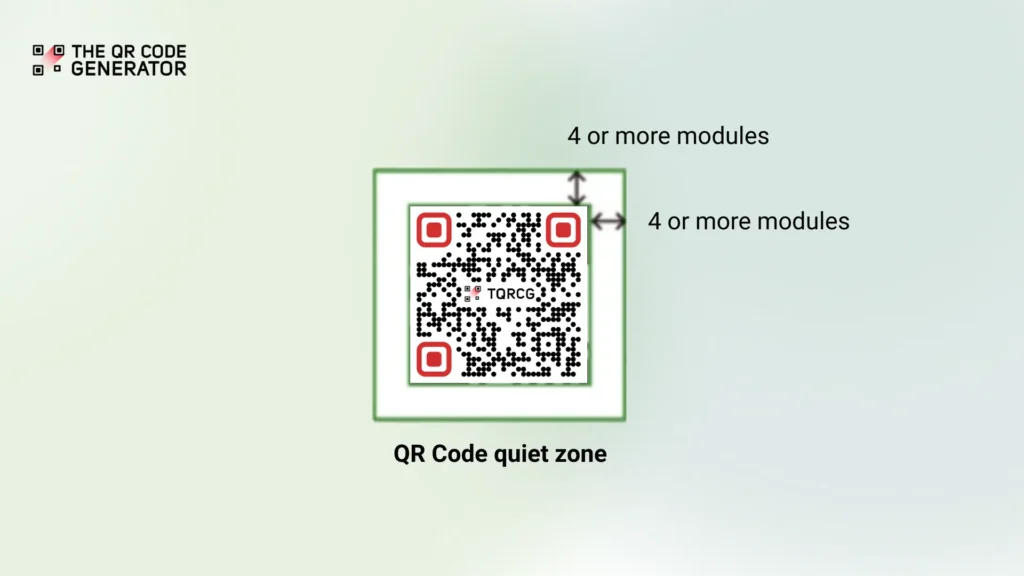
This standard asks for the QR Code quiet zone to have a white space border around your QR Code that is at least four modules wide on all sides.
And these modules? They are the basic unit of measurement for QR Codes. In practical terms, it’s the width of one of the tiny black or white squares you see when you look closely at a QR Code.
Here’s how the standard is applied:
Measure the width of any single black or white square in your QR Code. Then multiply the size of the module you get by four. Ensure this width exists on all four sides of your code.
For example, if your QR Code modules are two mm wide, your quiet zone must be at least eight (2 × 4) mm wide.
Along with the four module rule, ISO/IEC 18004 also recommends the following:
- Maximum contrast ratio between the quiet zone and the darkest QR Code elements
- Uniform application on all sides
- No interruption by other design elements
ISO/IEC 18004 mentions that anything below four modules might be scannable indoors in some instances, but can cause scannability issues across all these variables:
- Angled scanning (phones held at various angles)
- Variable lighting conditions
- Different scanner technologies
- Printed surface variations
Even though the guidelines seem straightforward, a QR Code quiet zone violation happens more often than you think.
What are the most common reasons for QR Code quiet zone violations?
Most QR Code quiet zone violations occur due to common errors. Spotting these issues before printing or publishing saves time, money, and customer frustration.
1. Text placement violations
The most common mistake is placing descriptive text too close to QR Codes. Phrases such as “Scan Here” or “View Menu” often encroach on the required quiet zone space.
2. Background pattern interference
Branded backgrounds pose significant challenges. Company logos, geometric patterns, and textured surfaces that extend into quiet zones create visual noise that confuses scanners.
3. Color contrast issues
While QR Code quiet zones don’t have to be pure white, they must maintain enough contrast with the QR Code’s dark elements. Businesses sometimes use light gray, cream, or even pale brand colors that technically meet contrast requirements but cause scanning problems in certain lighting conditions.
4. Size constraint compromises
Business cards, product labels, and social media graphics often force designers to choose between adequate quiet zones and other design elements. The wrong choice always results in scanning failures.
Techniques to ensure perfect quiet zone management (+ free checklist)
Implementing proper QR Code quiet zone requirements requires the right tools and systematic approaches. Here are the three methods to ensure consistent compliance.
1. The pencil test: Simple, quick, but not 100% reliable
Here’s a simple quality control method called the pencil test that catches quiet zone violations before they go to print:
- Step 1: Place a standard pencil (about 7 mm diameter) at any edge of your QR Code
- Step 2: Slowly roll it outward while maintaining contact with the surface
- Step 3: The pencil must roll at least one full rotation (about 22 mm) before encountering any text, graphics, or design elements
- Step 4: Repeat on all four sides
If the pencil overlaps something before completing one rotation, you have a quiet zone violation that needs addressing.
Similarly, use your cursor or a digital ruler to measure equivalent distances for digital applications. However, this method is a general indication, not a definitive answer, as it can sometimes be inaccurate.
2. The quiet zone checklist: Detailed, exhaustive, but not very simple to follow
You can use the following comprehensive testing checklist to verify that your QR Code implementation meets all quiet zone requirements.
The checklist covers everything from initial design template setup to compliance and testing, ensuring your codes scan reliably across different devices and conditions. It is thorough, and each step provides specific guidance to ensure your QR Code is quiet zone compliant.
Design template setup
Quality control verification
Multi-device and app testing
Environmental conditions testing
Performance benchmarking
While thorough, the checklist is by no means easy to follow. This is where TQRCG can help.
3. Using The QR Code Generator (TQRCG): Fast and accurate
All the steps in the quiet zone checklist will automatically be taken care of if you use The QR Code Generator (TQRCG) to create your QR Code.
TQRCG automatically applies proper quiet zone requirements to every code you create, eliminating guesswork and ensuring reliable scanning performance.
With built-in compliance features and professional templates, you can focus on your QR Code design and analytics while the tool handles the technical details that make your QR Codes work.
Built-in compliance features:
- Automatic four-module quiet zone application
- Visual indicators that show quiet zone boundaries during design
- Template library with pre-calculated spacing for typical applications
- Quality preview feature that simulates scanning conditions and flags your QR Code if designed in a way where it’s not scannable
Best practices to ensure a QR Code quiet zone across all mediums
Different platforms and printing methods present various challenges when maintaining quiet zones while ensuring reliable scanning.
Let’s break it down by medium first.
Medium specifications
Social media
Challenges: Limited space, image compression, platform constraints
Best practices:
- Use a minimum of 6-module quiet zones
- Test compressed versions before publishing
- Avoid overly intricate designs
Tip: Maintain contrast even after compression and test across all platforms.
Business cards
Challenges: Small size (3.5 × 2 inches), competing design elements
Best practices:
- Dedicate a clear area just for the QR Code
- Use corners/margins efficiently
- Consider folded designs for extra space
Tip: Minimum QR Code size 0.5 inches with proper quiet zones.
Product packaging
Challenges: Regulatory text, ingredient lists, branding competition
Best practices:
- Plan QR Code placement early in the design phase
- Create “no-go” zones where text and logos won’t overlap
- Use folds or flaps strategically
Tip: Always test on actual package sizes.
Digital signage
Challenges: Viewing distance, screen resolution
Best practices:
- Scale QR Codes proportionally
- Account for viewing angles
- Test from expected distances
Tip: Adjust module size to match viewing distance.
Print materials
Challenges: Surface texture, resolution limits, color constraints
Best practices:
- Use matte surfaces to avoid glare
- Maintain correct DPI
- Ensure a strong contrast between code and background
Tip: 300+ DPI for offset, 600 DPI for digital printing.
Mobile displays
Challenges: Screen glare, varied camera quality, app compatibility
Best practices:
- Use 6-module quiet zones
- Test on multiple devices and apps
- Optimize for arm’s length scanning
Tip: Ensure compatibility with iOS and Android native cameras.
Once we’ve optimized for various mediums, it’s time to consider how QR Codes perform in terms of print quality.
Print quality specifications
Higher print resolution creates sharper QR Code edges that scanners can detect more reliably, while certain surface materials can interfere with scanning algorithms.
| Printing method | Minimum DPI | Recommended surfaces | Avoid | Examples |
| Offset printing | 300 DPI minimum | Matte-coated paper, uncoated white | Glossy materials (creates light reflection that interferes with scanning) | Brochures, flyers |
| Digital printing | 600 DPI minimum | White vinyl stickers | Textured papers (blurs QR Code edges) | Office prints, small-batch marketing |
| Large format printing | 150 DPI minimum | Clean glass, acrylic | Transparent materials (poor contrast with background) | Banners, posters, signage |
| Screen printing | 200 DPI minimum | Smooth, high-contrast surfaces | Dark or colored substrates (reduces contrast) | T-shirts, promotional items |
What is DPI?
Dots per inch (DPI) is the resolution quality of printing. Higher DPI creates sharper, more defined QR Code edges that scanners can detect quickly. Lower DPI can cause blurry module boundaries that confuse scanning algorithms.
You have your medium and are armed with the print quality specs. Now, it comes down to the quiet zone’s color.
Quiet zone color specifications
While quiet zones don’t require pure white, they must maintain enough contrast with dark QR Code elements to ensure reliable scanning performance.
| Color option | Contrast requirement | Best use cases | Testing needed |
| Pure white | Optimal contrast | All applications | None |
| Light gray | Maximum 20% black | Subtle branding needs | Verify across lighting conditions |
| Pale brand colors | Maintain high contrast | Brand consistency required | Extensive device testing |
| Natural paper | Cream, off-white tones | Premium print materials | Test with various lighting |
Scan-perfect QR Codes with TQRCG
A quiet zone isn’t optional decoration, it’s part of the QR Code’s functionality. Respecting the four-module rule, testing across mediums, and using the right tools will make the difference between a scan and a lost opportunity.
Use the QR Code Generator to automatically apply proper quiet zone requirements to every code you create.
Create a fully functional QR Code with perfect quiet zones for free
Frequently asked questions
The international standard requires a minimum quiet zone of four module widths on all sides of a QR Code. A module is the width of the smallest black or white square in the code. For example, if each module in your QR Code is 2 mm wide, your quiet zone must be at least 8 mm wide on all sides.
No, you must never place design elements within the QR Code quiet zone. This includes text, logos, graphics, patterns, and other visual elements. The quiet zone must remain clear to allow scanners to properly detect the QR Code boundaries. Even subtle elements that seem invisible can interfere with scanning algorithms and cause failures. Place them outside the quiet zone perimeter if you need to include instructional text or branding.
Some QR Codes may scan successfully despite quiet zone violations due to ideal conditions such as perfect lighting, high-end scanning devices, or optimal angles. However, these QR Codes will fail frequently in real-world conditions with variable lighting, different devices, or typical user scanning behavior. Professional scanning equipment might overcome minor violations, but mobile device cameras, which most customers use, require proper quiet zones for consistent performance.
Violating quiet zone requirements results in scan failures. Users will experience frustration trying to scan your QR Code multiple times, often giving up entirely. This leads to lost sales opportunities, reduced campaign effectiveness, and negative brand perception. You might also need to reprint materials, provide manual alternatives, or deal with customer service issues related to non-functioning codes.
Regardless of QR Code colors, the four-module width requirement remains unchanged, but color usage adds contrast considerations. QR Code quiet zones need a high contrast with the QR Code’s darkest elements. While not necessarily white, the colors of the quiet zones must be on the lighter side. If using brand colors, test scanning performance across devices and lighting.