When it comes to QR Codes, the surface and printing method make all the difference.
Paper QR Codes can fade, smudge, or tear over time, while engraved or UV-printed codes on durable materials such as metal or tile can remain scannable for years. That’s why industries from manufacturing and logistics to retail and hospitality use them for permanent labeling, compliance, and premium branding.
This guide will explore the best surfaces for durable QR Codes, printing and engraving methods, and real-world applications to help you create codes built to last.
Table of contents
- Printing vs. engraving QR Codes: Which should you pick?
- Advantages of adding QR Codes on durable surfaces
- Choosing the right surface for durable QR Codes
- Common challenges of engraving QR Codes on durable surfaces
- Best techniques for adding QR Codes to different materials
- Best practices for creating durable QR Codes
- Industries where durable QR Codes make an impact
- Get started with durable QR Codes today
- Frequently asked questions
Printing vs. engraving QR Codes: Which should you pick?
| Criteria | Printing | Engraving |
| Durability | Moderate; may fade, smudge, or peel over time | Very high; permanent and tamper-proof |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial cost for equipment and setup |
| Visual options | Full color; vibrant designs possible | Limited color; natural etched appearance |
| Best use cases | Marketing campaigns, packaging, textiles | Industrial labeling, asset tracking, signage |
| Maintenance | May require replacement over time | Minimal to none |
| Environmental resistance | Varies by method; UV printing resists fading | Excellent resistance to weather, chemicals, and wear |
Advantages of adding QR Codes on durable surfaces
Printing or engraving durable QR Codes ensures long-term reliability and functional use cases that paper or digital QR Codes simply can’t match.
Here’s why businesses prefer them over standard materials:
1. Durability and permanence
Laser-engraved QR Codes on long-lasting materials resist fading, peeling, smudging, or warping. They stay scannable even after exposure to harsh weather, frequent handling, or industrial conditions, making them ideal for long-term applications.
2. Professional branding
Materials like metal, wood, or glass give a premium feel. Laser-etched business cards, polished plaques, or sleek signage attract attention and convey quality, allowing QR Codes to become a stylish part of your brand experience.
3. Industrial compliance
In manufacturing and logistics, QR Codes help maintain compliance and accountability. They can display safety data sheets (SDS), instructions, and manuals while acting as permanent identifiers that withstand harsh environments—perfect for audits, inventory tracking, and regulatory adherence.

4. Customer engagement
Durable QR Codes provide a reliable link between offline and online interactions on retail packaging or point-of-sale surfaces. Consistently scannable codes let customers access promotions, product details, or loyalty programs, and dynamic QR Codes allow updates to offers anytime. QR Code generators like The QR Code Generator (TQRCG) make it easy to create dynamic codes that can be updated without reprinting.
5. Cost-effectiveness
Although engraving carries higher upfront costs than ink-based prints, the long-term savings are significant. Durable QR Codes reduce the need for frequent reprints or replacements, making them a one-time investment with lasting returns in both efficiency and brand impact.
Choosing the right surface for durable QR Codes
QR Codes are highly versatile and can be printed on a wide range of surfaces, depending on their intended use. Choosing the right material affects both longevity and consistent scannability across different environments.
Here are some of the most common materials:
1. Metal
Metal is one of the most durable options. Stainless steel and aluminum resist corrosion, heat, and heavy usage, making them ideal for industrial labels, machine identification plates, and equipment inventory markers. Metal business cards with QR Codes are also gaining popularity for their premium, high-quality feel.
2. Durable plastics
High-quality plastics offer excellent durability and flexibility, making them ideal for product packaging to share information, logistics labels, ID cards, and promotional items. They maintain QR Code integrity during shipping and everyday handling while being cost-effective for mass production.
3. Glass
Glass provides exceptional durability with a premium aesthetic appeal. It’s commonly used for window decals, storefronts, and high-end product packaging where QR Codes need to withstand weather exposure while maintaining a professional appearance.
4. Wood
Wood offers a natural, eco-friendly option with a unique aesthetic appeal. When properly treated, it works well for hospitality applications, decorative items, and premium packaging where the organic feel aligns with brand values.
5. Cloth
QR Codes on clothing are popular for promotions, brand engagement, and garment authentication. Specialized printing methods like embroidery or heat-transfer vinyl ensure codes remain legible after repeated washing, making them ideal for events and marketing campaigns.
6. Paper and cardboard
While less durable, paper and cardboard are cost-effective for temporary applications like event tickets, product packaging, and short-term promotional materials, where codes only need to function for limited periods.
Common challenges of engraving QR Codes on durable surfaces
While durable QR Codes provide lasting value, there are some challenges you should keep in mind. Understanding these pain points can help you choose the right surface and avoid common pitfalls.
1. Reflective glare on tiles and metals
A frequent issue when engraving QR Codes on shiny metal or glazed tile surfaces is reflective glare. The high reflectivity can cause scanners and smartphone cameras to struggle with focusing, which can lead to unsuccessful scans. To overcome this, it’s best to use matte, anti-glare coatings, or etched engravings.
2. Wear and tear after regular use
Despite being extremely durable, inevitably, physical damage like scratches, scuffs, and fading from sun or weather exposure can degrade QR Codes on any surface. Outdoor or industrial environments are especially prone to such damage. This can lead to QR Codes that no longer scan. To avoid this, create QR Codes with a higher error correction level so that even if they’re damaged a bit, they will work for you longer.
💡 Pro tip: With The QR Code Generator (TQRCG), you don’t need to adjust these levels yourself. The platform automatically applies the correct error correction for your use case, ensuring your QR Codes stay scannable wherever they’re placed. Just choose your QR Code type and create one.
In addition, it automatically checks and prompts you when you customize your QR Code in a way that impacts its scannability.
3. Curved or uneven surfaces distort codes
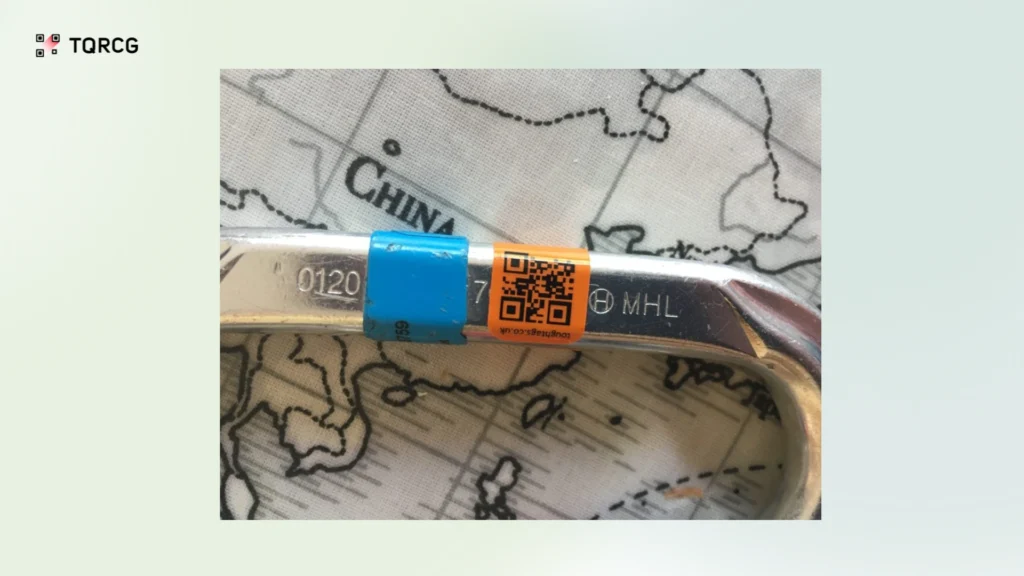
Adding QR Codes on curved or irregular surfaces like bottles, pipes, or fabric can distort the code pattern. This distortion causes parts of the code to misalign, making scanning difficult or impossible. To address this, use fewer data elements to create simpler codes with larger modules, and increase the size of the QR Code to accommodate surface curvature without losing scannability.
4. Poor contrast or visibility
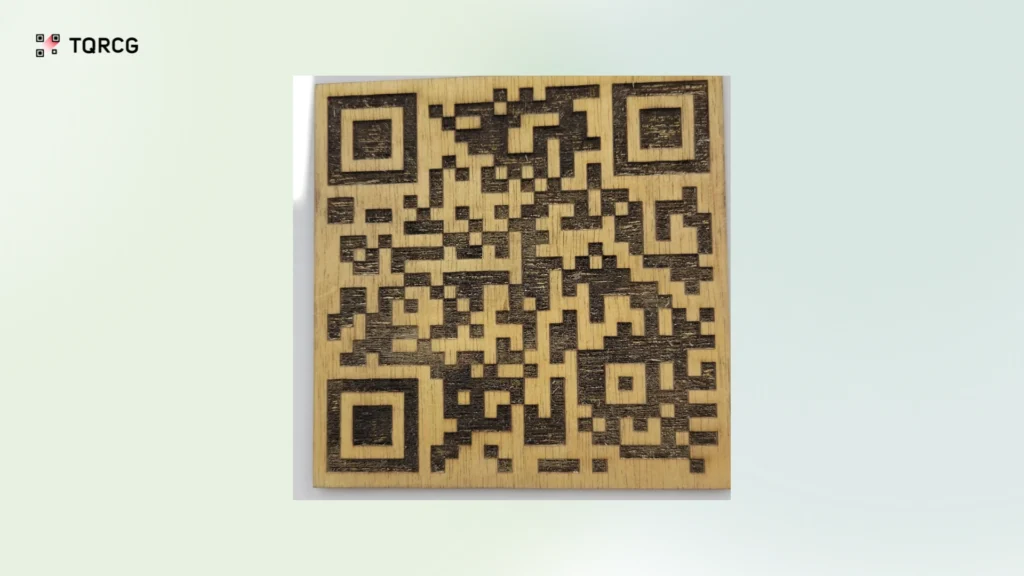

Low contrast between the QR Code and the background surface creates scanning difficulties. This is especially problematic on wood, where engraving may not create sufficient color difference, or on dark metals, where codes blend with the surface. Many users have shared struggles with engraving QR Codes where the code’s fine details blur or blend with the background, making scans unreliable. Always ensure high contrast (dark codes on light backgrounds work best).
5. Size limitations on small surfaces
The minimum size requirements for QR Codes often pose a challenge, particularly when space is limited. The individual modules become too tiny for cameras to resolve clearly. This issue is common on metal labels and vCard QR Codes on business cards, where space is premium. Plan for a slightly larger QR Code or use higher error correction levels to help balance size constraints without sacrificing functionality.
6. Surface preparation and finish quality
Poorly prepared surfaces or inconsistent engraving depth can cause parts of the code to be illegible. This is common with DIY engraving on varied materials where depth, speed, or power settings aren’t optimized for the specific surface material. Ensure clean, precise engraving with consistent depth across the entire code area.
By proactively addressing these engraving challenges, you can ensure that QR Codes remain effective, maintaining functionality and customer trust over time.
There are now many methods of engraving QR Codes. Let’s look at the most common ones to help you decide.
Best techniques for adding QR Codes to different materials
Choosing the right technique for applying durable QR Codes is crucial. Different materials and use cases require specific methods that balance durability, cost, and visual quality.
Below are the most popular and effective techniques used today:
1. Laser engraving and fiber laser engraving
This method uses lasers to etch the QR Code permanently into surfaces such as metal, wood, and glass. It offers extremely high durability and tamper-proof results with excellent detail. The upfront cost is higher, typically ranging from $3,000 to $15,000 for laser engraving machines, though per-unit costs vary depending on volume. It’s ideal for industrial labels, machinery marking, and asset tracking where endurance is critical.
2. High-contrast etching
This technique enhances scannability by creating deep, precise marks that reduce glare, primarily on metal, glass, and wood surfaces. It offers high durability at a medium cost but has limited color options. The deep etching creates a strong contrast between the code and background, making it especially useful for outdoor signage or areas prone to reflective glare.
3. UV printing
UV printing produces high-contrast, full-color QR Codes suitable for plastics, metal, glass, and signage. It supports vibrant branding and design flexibility at a medium-high cost, usually around $5–$15 per print, depending on size and complexity. However, it is less durable than engraving outdoors, as prints may fade with sun exposure, making it perfect for premium packaging and indoor signage.
3. Screen printing
Screen printing pushes ink through a mesh screen to create vibrant QR Codes on cloth, plastics, or indoor signage. It is cost-effective, especially for bulk printing. The method has moderate durability and isn’t water-resistant, limiting its application to temporary or indoor promotional uses and textiles.
4. Adhesive QR Code stickers
Stickers offer a low-cost, easy-to-apply solution on paper, plastics, and packaging. While fast to deploy, stickers can peel or fade over time and are less durable, making them best suited for short-term promotions and labeling.
Each method has clear advantages and trade-offs. Selecting the best method depends on your budget, durability requirements, and the expected lifespan of the QR Code.
The list below will help you quickly identify the best QR Code printing method based on your needs.
| Scenario | Best method | Reason |
| Industrial/heavy duty | Laser Engraving | Permanent, tamper-proof, withstands harsh conditions |
| Outdoor/high glare | High-Contrast Etching | Deep marks reduce glare, weather-resistant |
| Branding/customer-facing | UV Printing | Colorful, high contrast, visually appealing |
| Bulk/textile applications | Screen Printing | Cost-effective for large quantities, works on fabric |
| Short-term/promotional | Stickers | Affordable, quick deployment, easy application |
Best practices for creating durable QR Codes
Creating QR Codes that last and perform well requires more than just choosing the right surface or printing method.
Let’s look at some best practices you can follow to ensure a strong return on investment (ROI) from QR Code initiatives.
1. Use dynamic QR Codes for flexibility
Opt for dynamic QR Codes whenever possible. Unlike static codes, dynamic QR Codes can be updated or changed remotely without reprinting. This flexibility saves cost and effort in the long run, especially when marketing campaigns or product information evolve.
2. Test scannability before production
Before final production, test QR Codes under various real-world conditions, including lighting scenarios (bright sunlight, shadows, artificial light), scanning angles, and smartphone cameras. This step ensures the code can be scanned reliably in its intended environment, helping avoid costly reprints and user frustration.
💡 Pro tip: Generate test codes with The QR Code Generator to validate performance before committing to permanent engraving.
3. Optimize size and quiet zone requirements
Ensure the physical size of the QR Code matches scanning distance requirements. A typical minimum size is about 1 × 1 inch for handheld scanning. Also, maintain an adequate “quiet zone” (empty margin) around the code to help scanners detect it without interference.
4. Maximize contrast and minimize glare
Use a dark QR Code on a light, preferably matte background to maximize contrast and reduce glare. High contrast between the code and its background is critical for scanners to differentiate modules clearly. Avoid glossy or reflective finishes that can cause scanning difficulties due to light reflection, especially in outdoor environments.
5. Choose appropriate surfaces and placement
Avoid curved, uneven, or highly textured surfaces that can distort the QR Code pattern and make it unreadable. Whenever possible, print on flat, smooth surfaces. If a curved surface is unavoidable (such as cylindrical bottles), increase the QR Code size significantly and position it to minimize distortion across the viewing area.
6. Select weather-resistant materials for outdoor use
For QR Codes exposed to sun, rain, or harsh environments, select printing methods and materials that resist UV fading, water damage, and physical abrasion. Consider weatherproof inks, protective laminates, or permanent engraving options to preserve code integrity and maintain scannability over time.
7. Follow industry standards when required
In regulated or compliance-sensitive industries, adhere to ISO/IEC 18004 and GS1 standards for QR Codes. This ensures interoperability and traceability, and meets audit requirements for applications like asset tracking, logistics, and product labeling. Standard compliance also improves compatibility across different scanning devices and software.
8. Implement appropriate error correction
Choose higher error correction levels (M or H) for codes that may experience wear, damage, or partial obstruction. While this increases the code’s complexity, it allows successful QR Code scanning even when up to 15-30% of the code is damaged or obscured, significantly extending the functional lifespan of durable QR Codes.
Industries where durable QR Codes make an impact
Durable QR Codes aren’t just a convenience—they’re a strategic tool that keeps operations running smoothly and enhances user experience across various industries. These resilient codes add value wherever reliability matters, from tracking inventory to providing lasting customer information.
The sectors that benefit are:
1. Manufacturing and logistics
QR Codes were invented to streamline and track automotive parts while being manufactured. Durable QR Codes are critical in manufacturing and logistics for asset tracking, compliance, and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applications.
By placing engraved or printed codes on machinery, raw materials, and finished goods, companies can streamline equipment maintenance and track inventory in real time while ensuring regulatory compliance. QR Codes often link to digital maintenance logs, certifications, and safety information, reducing downtime and enhancing operational visibility.
2. Luxury brands

Retailers and luxury brands use durable QR Codes to authenticate products and elevate customer engagement. Brands such as Ralph Lauren use QR Codes on their tags to assure customers of authenticity and combat counterfeiting. Coach also uses QR Codes to make their customers aware of their personalized services.
3. Healthcare and pharmaceuticals
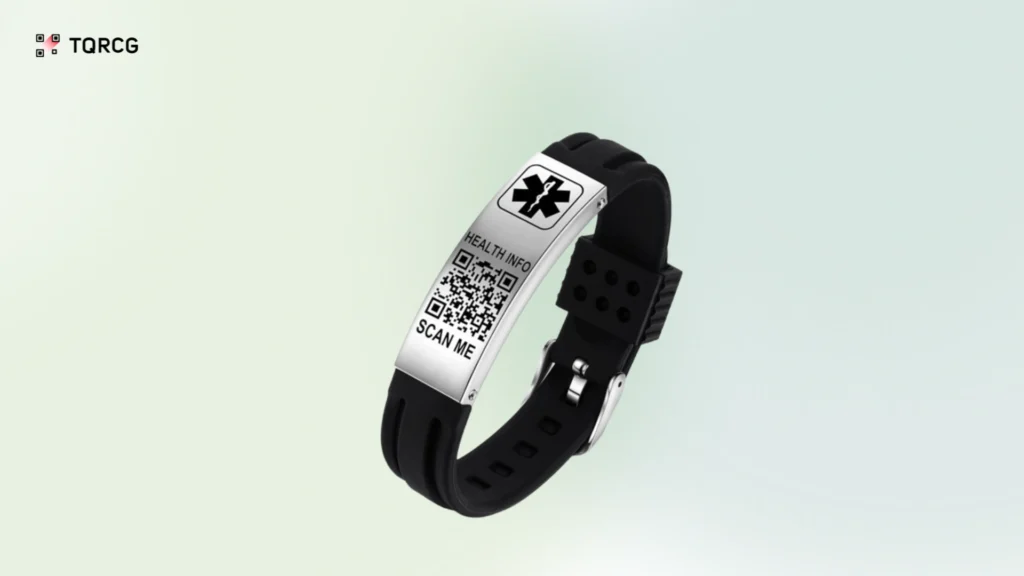

QR Codes help with equipment tracking, medication management, and regulatory compliance in healthcare. Medical devices feature QR Codes for unique device identification (UDI) and enable tracking from manufacturing to patient use. Metal QR Codes are used on medical ID bracelets by patients to convey health information and allergies.
4. Retail and e-commerce
Durable QR Codes on cardboard packaging and shipping labels enable better inventory control and customer engagement. Retail and e-commerce companies embed QR Codes to provide product information and facilitate easy returns. Durable QR Codes ensure seamless tracking and post-sale service in varied transit conditions. Retailers use QR Codes for interactive shopping experiences as well as for inventory management.
5. Government and infrastructure

Governments use durable QR Codes for infrastructure management, road signage, and public information. QR Codes on roads, bridges, and public assets provide instant access to maintenance records and allow them to connect with citizens. For example, Melbourne used metal QR Codes to allow citizens to report street waste and vandalism in the area.
Get started with durable QR Codes today
Printing durable QR Codes is a smart move for any business that wants its codes to last and stay scannable over time. Whether you choose laser engraving for a permanent industrial solution or UV printing, the key is picking the right combination of surface and method for your needs.
Durable QR Codes help build trust, improve compliance, and create smooth customer experiences that keep people coming back. Of course, challenges such as glare, contrast, and size must be managed carefully, but with the right preparation and printing technique, these can be easily overcome.
If you’re ready to create durable and dynamic QR Codes, start with a reliable QR Code generator like The QR Code Generator (TQRCG).
Frequently asked questions
QR Codes work on almost any surface, but metals and tiles are the most durable. If you need QR Codes at scale, plastics and product packaging are more practical. For short-term campaigns, paper or cardboard also works.
Yes. Laser-engraved QR Codes on metal are long-lasting and resistant to weather, heat, and chemicals. They remain scannable even in tough industrial environments, making them ideal for asset tracking or equipment labeling.
They do, but glare can sometimes make scanning harder. Using a matte finish or high-contrast colors (like black on white) solves the issue and ensures smooth scanning.
Laser engraving and UV printing are the most reliable methods for outdoor use. Both methods resist fading, rain, and sunlight, unlike paper stickers or regular ink prints.
Yes. Even though the engraved pattern is fixed, the QR Code itself can be dynamic. That means you can update the linked content anytime without re-engraving. QR Code Generator (TQRCG) offers two free dynamic QR Codes that can be used for engraving.
Many industries like manufacturing, logistics, construction, healthcare, retail, and hospitality rely on durable QR Codes. These industries use them for asset tracking, packaging, safety information, and customer engagement.