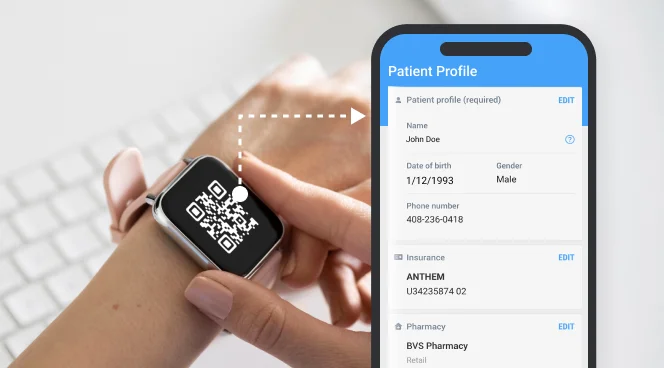
- QR Code Generator
- Scan
-
Solutions
-
Resources
- Pricing
-
Scheduling & Forms
-
 Calendly
Calendly
-
 Google Forms
Google Forms
-
 Microsoft Forms
Microsoft Forms
-
 SurveyMonkey
SurveyMonkey
-
Files & Apps
-
 Google Drive
Google Drive
-
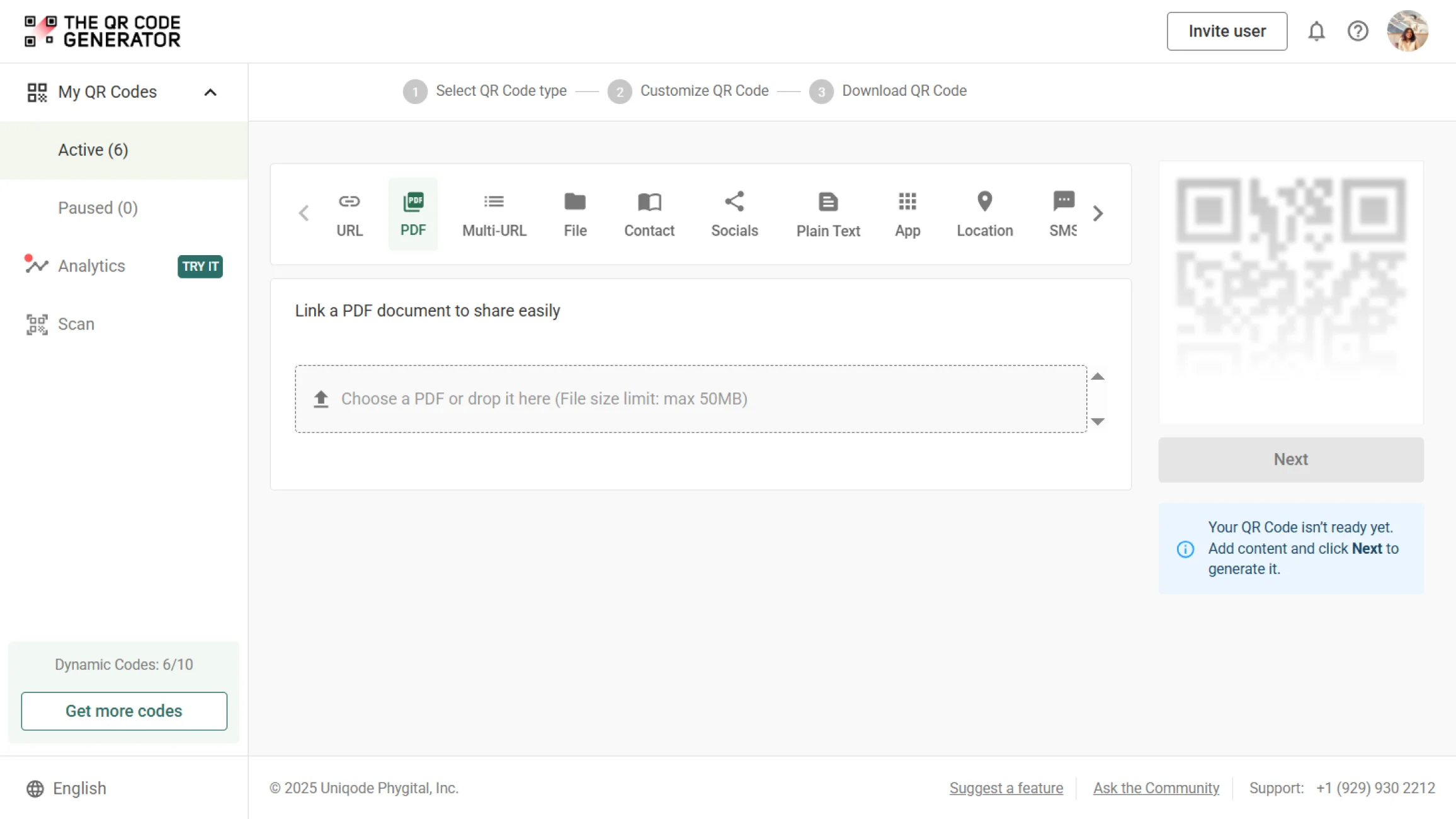
 PDF
PDF
-
Reviews
-
 Google Reviews
Google Reviews



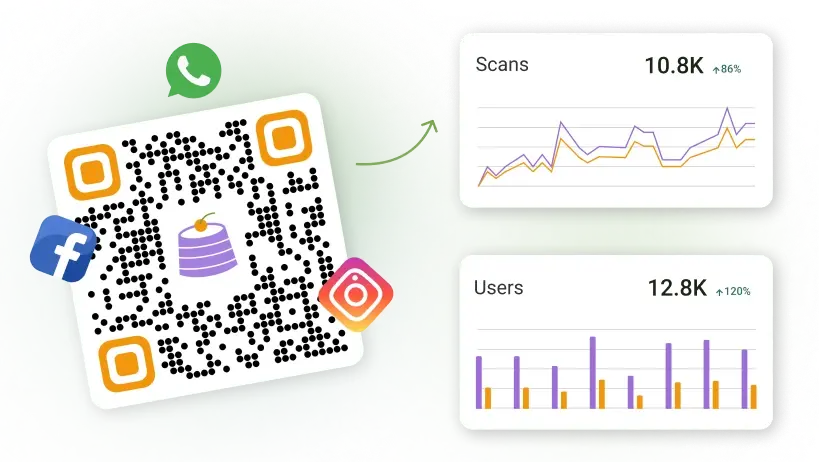





 No credit card required
No credit card required